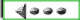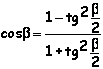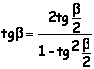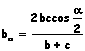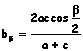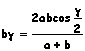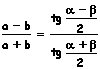Qui di seguito sono riportate le formule di maggior importanza che si sono incontrate durante l'anno
|
GRADI |
0° |
18° | 30° | 45° | 60° | 90° |
135° |
150° |
180° |
270° |
360° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RADIANTI |
0 |
π/10 |
π /6 | π /4 |
π /3 |
π /2 |
3π/4 |
5π/6 |
π |
3π/2 |
2π |
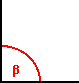 ANGOLO
RETTO(
β= 90°) ANGOLO
RETTO(
β= 90°) |
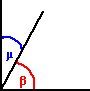 ANGOLI
COMPLEMENTARI (β
+ μ
= 90°) ANGOLI
COMPLEMENTARI (β
+ μ
= 90°) |
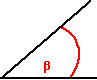 ANGOLO
ACUTO ( β<
90°) ANGOLO
ACUTO ( β<
90°) |
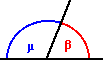 ANGOLI
SUPPLEMENTARI (β+
μ=
180°) ANGOLI
SUPPLEMENTARI (β+
μ=
180°) |
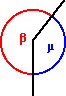 ANGOLI
ESPLEMENTARI ( β+
μ
= 360°) ANGOLI
ESPLEMENTARI ( β+
μ
= 360°) |
| ANGOLI COMPLEMENTARI | |
|
|
| ANGOLI CHE DIFFERISCONO DI UN ANGOLO RETTO | |
|
|
| ANGOLI SUPPLEMENTARI | |
|
|
| ANGOLI CHE DIFFERISCONO DI UN ANGOLO PIATTO | |
|
|
| ANGOLI CHE HANNO PER SOMMA TRE ANGOLI RETTI | |
|
|
| ANGOLI CHE DIFFERISCONO DI TRE ANGOLI RETTI | |
|
|
| ANGOLI ESPLEMENTARI | |
|
|
| ANGOLI OPPOSTI |
|
| VALORI | ||||
| noto | sin β | cos β | tg β | ctg β |
| sin β | sinβ |
|
|
|
| cos β |
|
cos β |
|
|
| tg β |
|
tgβ |
|
|
| GRADI | RADIANTI | SENO | COSENO | TANGENTE | COTANGENTE |
| 0° | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | non esiste |
| 15° | |||||
| 18° | |||||
| 22°30' | |||||
| 30° | |||||
| 36° | |||||
| 45° | 1 | 1 | |||
| 60° | |||||
| 75° | |||||
| 90° | 1 | 0 | non esiste | 0 |
|
Formule di sottrazione |
Formule di addizione |
|
sin(α-β) = sinαcos β - cosαsinβ |
sin(α+β) = sinαcosβ + cosαsinβ |
|
cos(α-β) = cosα cos β + sin αsin β |
cos(α+β) = cosαcos β - sin αsin β |
|
tg(α-β)=(tg α - tg β)/(1 + tg αtg β) |
tg(α+β) = (tg α + tg β)/(1 - tg αtg β) |
|
Formule di duplicazione |
|
sin2β = 2 sin β cos β |
|
cos2 β = cos2β - sin2β = 1 - 2sin2β = 2cos2β - 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
Formule di bisezione |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Formule di prostaferesi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[con p e q |
|
[con p e q |
|
Formule di Werner |
|
sin μcos β
= |
|
cos μcos β
= |
|
sinμsin β
= |
β
|
Espressione di sinβ, cosβ, tgβ, ctg β, in funzione razionale di tg(β/2) |
|
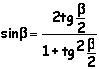 |
|
|
|
|
|
Relazioni tra gli elementi di un triangolo rettangolo |
|
| b = a sin β | c = b cos β |
|
b = c tg β |
c = b ctg β |
|
Teorema della corda |
|
AB = 2r sin β |
|
Teorema dei seni (o di Eulero) |
|
|
|
Teorema del coseno (o di Carnot) |
|
a2 = b2 + c2 - 2 bc cos α b2 = a2 + c2 - 2 ac cos β c2 = a2 + b2 - 2 ab cos γ |
|
Teorema di Nepero |
|
|
|
Formule di Briggs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|